African swine fever remains the key driver impacting the global animal protein market, despite the effects of COVID-19 on demand, Rabobank’s latest African Swine Fever Update has shown.
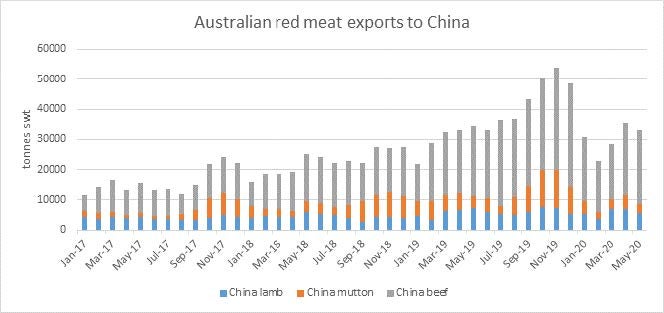
And this is being borne out in Australia’s red meat exports to China, which remain strong, according to latest figures.
The Rabobank update said African swine fever was still the major influence on global pork markets, and it continued to impact pig herds and restrict pork production in China, Vietnam, the Philippines and parts of eastern Europe.
Despite Australia’s total red meat exports being down 16 per cent year-on-year in May, exports to China are down only four per cent – reflecting strong Chinese demand in the wake of African swine fever, despite disruptions due to COVID-19.
Rabobank senior proteins analyst, Angus Gidley-Baird said considering Australia’s reduced production, current export figures highlight China’s strong appetite for Australian protein.
“While exports into China are not quite at the levels they were at the end of last year – when African swine fever-driven pork shortages were driving strong Chinese demand and Australian production was much higher – they are close to levels seen at the start of 2019, which is a positive outcome for the domestic industry,” Mr Gidley-Baird said.
China’s pork production is expected to decline by a further 15 to 20 per cent in 2020, while in Vietnam and the Philippines, declines are expected to be close to 10 per cent, prompting further import demand from these countries.
In China, Mr Gidley-Baird said, pork imports were expected to reach record levels, while imports of other animal protein types would also be strong.
“China’s pork import growth accelerated in the first four months of 2020, with meat imports up 180 per cent, year-on-year, and variety meat imports up 29 per cent year-on-year,” he said.
Rabobank maintained its view that China’s pork imports would reach a record level of about 3.5 million metric tonnes in 2020, with the majority of product supplied from the US, under the US/China ‘phase one’ trade deal.
However, Mr Gidley-Baird said imports for the rest of 2020 were still full of uncertainty, with disruptions to pork production and logistics in exporting countries, and movement in China’s domestic pork prices.
He said imports could ease through the current quarter, picking up again in quarter three and quarter four.
“But, COVID-19 and slower economic conditions aside, the protein gap created by African swine fever provides a strong demand force that will help support prices for Australian red meat exports for the remainder of 2020,” Mr Gidley-Baird said
“African swine fever will continue to underpin Chinese demand for Australian sheep and beef exports, as consumers look to substitute pork with alternative protein options.”
Rabobank Australia & New Zealand is a part of the global Rabobank Group, the world’s leading specialist in food and agribusiness banking. Rabobank has more than 120 years’ experience providing customised banking and finance solutions to businesses involved in all aspects of food and agribusiness. Rabobank is structured as a cooperative and operates in 40 countries, servicing the needs of approximately 10 million clients worldwide through a network of more than 1000 offices and branches. Rabobank Australia & New Zealand is one of Australasia’s leading agricultural lenders and a significant provider of business and corporate banking and financial services to the region’s food and agribusiness sector. The bank has 93 branches throughout Australia and New Zealand.
Media Contacts:
Denise Shaw
Head of Media Relations
Rabobank Australia & New Zealand
Phone: 02 8115 2744 or 0439 603 525
Email: denise.shaw@rabobank.com
Georgina Poole
Acting Media Relations Manager
Rabobank Australia & New Zealand
Phone: 0418 216 103
Email: georgina.poole@rabobank.com
